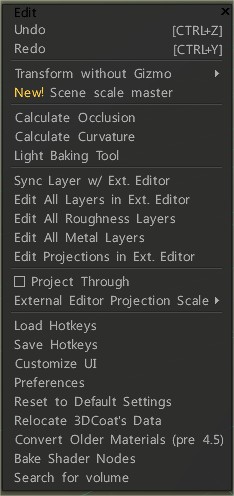
Undo: hotkey Ctrl+Z
Redo: hotkey Ctrl+Y
Transform without Gizmo:
These menu items are intended for assigning hotkeys to transform objects without the gizmo.
1) Press END over the required menu item, and assign the hotkey.
2) Press that hotkey and transform the object.
3) Press SPACE to enter numerical values (if this is a one-dimensional transform).
4) Press SHIFT, CTRL or CTRL+SHIFT for the discrete transform.
5) Press ESC or RMB to cancel the transform.
6) Press LMB to complete the transform.
When you transform the objects using this method, overview of the editing menu in which you will learn about the main editing functions and setting up the scene, you may use hotkeys (regardless of how they are assigned in 3D-Coat)
W – Activate free translation.
E – Activate free rotation.
R – Activate free scaling.
X, Y (or C), Z – Act along the axis for the translation, rotation or scaling, in dependence on the current mode.
– If you are in the translation mode:
X, then Y or SHIFT Z, or ZZ – move an object in plane XY.
Y, then Z or SHIFT X, or XX – move an object in plane YZ.
Z, then X or SHIFT Y, or YY – move an object in plane ZX.
F – Pick new pivot of the transformation.
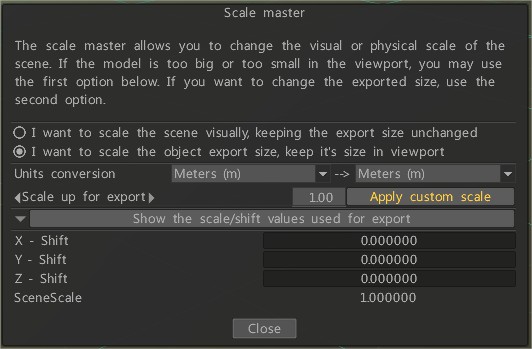
Scale Master
The scale master allows you to change the visual or physical scale of the scene.
If the model is too big or too small in the viewport, you may use the first option below.
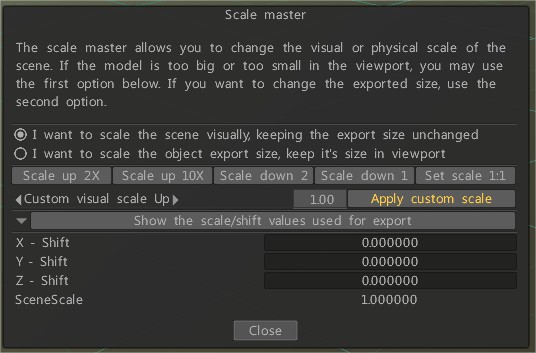
If you want to change the exported size, use the second option.
Calculate Occlusion
Calculate Occlusion baker runs a routine that calculates “Ambient Occlusion” (global illumination) based on tracing a number of light rays surrounding an object.
Calculate Curvature
Calculate Curvature: The curvature layer is required to use cavity/curvature as a condition for materials or conditional painting. The command will update the cavity/curvature layer using the current displacement and normal map.
Light Baking Tool
Light Baking Tool: Sometimes you need to bake all lighting into the diffuse color of the texture.
Open shader ball for example, fill layer with any reflective Smart Material, bake your reflection and it creates reflection layer in texture.
Sync layer with the external editor: This command allows you to synchronize the current layer with an external editor. You can set the path to the editor in Preferences. (The default is Adobe Photoshop.) The alpha channel will contain the transparency mask.
When you call on this command, the program Adobe Photoshop will open automatically with your file. Then you can change it and jump back to 3DCoat by pressing CTRL+S.
Edit All Layers in Ext. Editor: Edit all layers in an external editor. You can change the editor in the Options menu (Adobe Photoshop by default). This editor should be able to edit PSD files.
The texture will be stored as layers and opened as a PSD file in the external editor.
Then you can edit the texture and even add new layers. When you save it, 3DCoat will automatically reload it. Hotkey Ctrl+P
Edit All Roughness/Glossiness Layers: Edit all Roughness/Glossiness layers in an external editor.
Edit All Metal Layers: Edit all Glossiness layers in an external editor.
Edit Projections in Ext. Editor: You can edit the current projection in Adobe Photoshop using layers. You can change the editor in the Preferences menu (Adobe Photoshop by default).
This editor should be able to edit PSD files. The texture will be stored as layers and opened as a PSD file in the external editor. Then you can edit the texture and even add new layers.
When you save it, 3DCoat will automatically reload it. Hotkey Ctrl+Alt+P
When importing a PSD file into Clip Studio Paint, Affinity Photo or Krita; the layer order can sometimes be disrupted, meaning the layers may not appear in the same sequence as they did in Photoshop, potentially placing layers on top of each other that were originally below.
This is a known issue that can occur due to slight differences in how the software handles layer hierarchy.
Project Through: Project the image through all objects, even back faces.
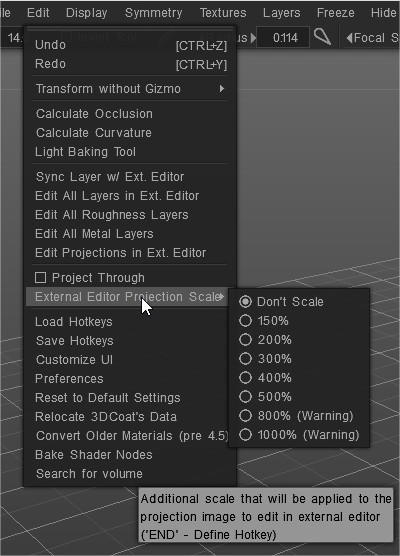
External Editor Projection Scale: Additional scale that will be applied to the projection image to edit in an external editor.
Load Hotkeys: Load hotkeys from the file.
Save Hotkeys: Save hotkeys from the file.
Customize UI: Remove/customize UI element.
Preferences: Set Hotkeys, Autosave time, External 2D-Editor, UI colors, and more…
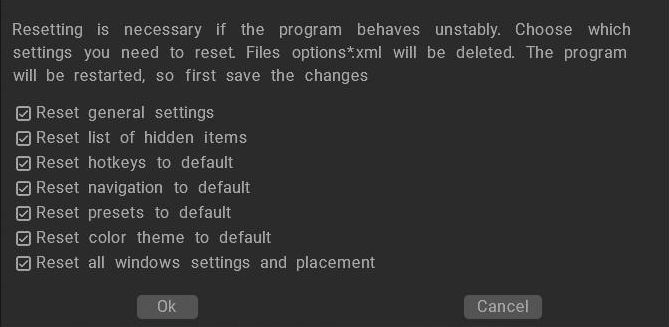
Reset to default settings: Resetting is necessary if the program behaves unstably. Choose which settings you need to reset. Files options*.xml will be deleted. The program will be restarted, so first, save the changes.
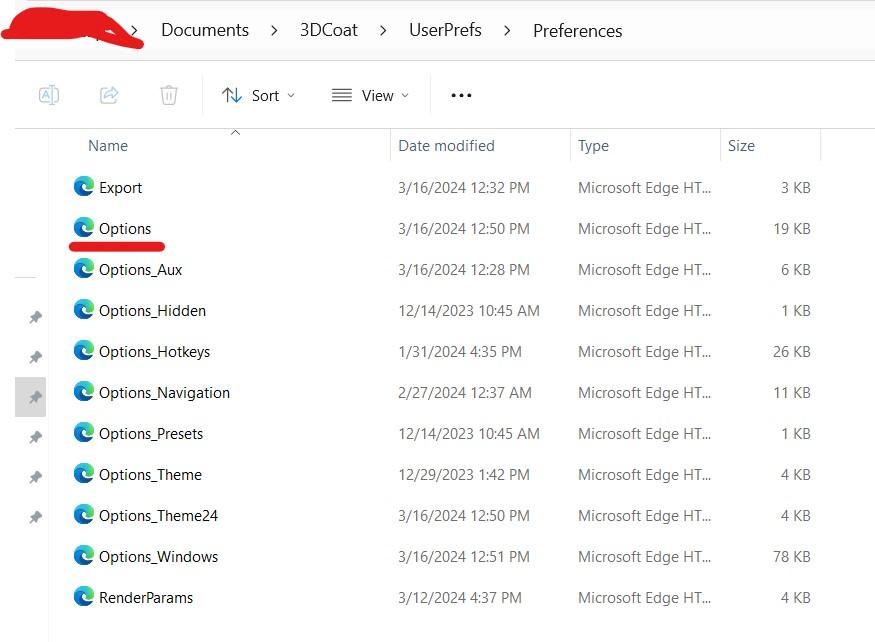
You can also try deleting the Options.xml file.
Make sure 3DC is closed when you do this. 3DCoat will auto create a new options.xml file when reopening 3DCoac.
Location of options.xml file shown in picture.
Relocate 3DCoat’s data: Edit Data Placement.
Convert Older Materials (pre 4.5): Convert Older Materials (pre 4.5)
Bake shader nodes: Bake shader nodes to real color/displacement. It may be helpful for the export.
Search for volume:
Tutorials
Quick Tip AO Baking Troubleshooting: This video demonstrates a Quick Tip about troubleshooting AO baking in 3DCoat, should a user encounter an unreasonable amount of lag.
AO Baking w/ OpenCL & Normal Map utilization: This video covers two major new improvements to AO baking in 3DCoat 4.5. OpenCL acceleration and Normal Map utilization.
Krita and 3DCoat workflow By Paul Geraskin.
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά  English
English Українська
Українська Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Português
Português Italiano
Italiano Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 (台灣)
中文 (台灣) Dansk
Dansk Slovenčina
Slovenčina Türkçe
Türkçe Nederlands
Nederlands Magyar
Magyar ไทย
ไทย हिन्दी
हिन्दी Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Eesti
Eesti Čeština
Čeština Română
Română Norsk Bokmål
Norsk Bokmål