Τα Έξυπνα Υλικά σάς επιτρέπουν να ζωγραφίζετε με φυσικά ακριβή υλικά, καθώς και να τα δημιουργείτε. Μπορούν να προβληθούν στο πλέγμα σας με διάφορες μεθόδους και επιτρέπουν τη βαφή προηγμένων υφών πολύ γρήγορα.
Χρήση Έξυπνων Υλικών στο 3DCoat 2022 : Το βίντεο δείχνει πώς λειτουργούν τα Έξυπνα Υλικά στο 3DCoat.
Πώς εφαρμόσατε το χαλάκι σε διαφορετικά αντικείμενα του ίδιου μοντέλου;
– Το 3DCoat σάς επιτρέπει να το κάνετε αυτό μέσω του συστήματος στρώσεων του αυτόματα. Εάν θέλετε κάτι να εφαρμόζεται μόνο σε ένα συγκεκριμένο μέρος, κρύψτε μερικά αντικείμενα βαφής ή καλύψτε το στρώμα… αυτή είναι η κύρια δύναμη του παλτού σε αντίθεση με άλλα προγράμματα.
– Το 3DCoat θα επιτρέψει στον χρήστη να επιλέξει τα αντικείμενα (συνεχόμενα πλέγματα) και να τα γεμίσει με ένα Έξυπνο Υλικό χρησιμοποιώντας το εργαλείο FILL. Μπορείτε επίσης να κάνετε κλικ σε μεμονωμένα κελύφη/νησιά UV στο 2D Texture Editor, αν προτιμάτε να εργάζεστε με αυτόν τον τρόπο. Υπάρχουν και άλλες επιλογές, όπως το γέμισμα όλων (ορατό στη σκηνή) σε ένα μόνο στρώμα, το γέμισμα με χάρτη UV κ.λπ.

– Ονομασία Έξυπνων Υλικών στη λίστα υλικών.

Έξυπνα υλικά γρήγορης εκκίνησης :
Επιλογή προεπισκόπησης
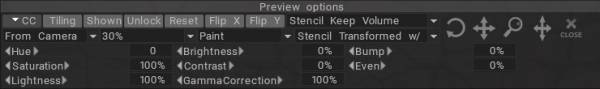
Επιλογές προεπισκόπησης : Εάν επιλέξετε να εμφανίσετε μάσκα/υλικό σε τουλάχιστον ένα από τα κανάλια (βάθη ή/και χρώματα ή/και γυαλάδα, δείτε περισσότερες λεπτομέρειες σχετικά με αυτά παρακάτω), εμφανίζεται ένας νέος πίνακας στην κορυφή.
Painting με υλικά
Και τα 3 Κανάλια Ζωγραφικής, όταν είναι ενεργοποιημένα, θα αντιδρούν με οποιοδήποτε υλικό που έχει επιλεγεί αυτήν τη στιγμή από τον Πίνακα Υλικών.
Κάθε υλικό μπορεί να περιέχει ξεχωριστή υφή για κάθε κανάλι του: Χρώμα, Βάθος και Γυαλάδα.
Εάν δεν έχει επιλεγεί κανένα υλικό (απενεργοποιήστε τη χρήση των Υλικών κάνοντας κλικ στο μεγάλο «X» στον Πίνακα Υλικών), τότε κάθε Κανάλι Ζωγραφικής θα απαντήσει με βάση το οποίο έχει επιλεγεί το Brush Alpha.
Τα Έξυπνα Υλικά σάς επιτρέπουν να δημιουργείτε και να ζωγραφίζετε με έξυπνα υλικά απόδοσης φυσικής βάσης. Αυτά τα υλικά αποτελούνται από πολλαπλές παραμέτρους για την επίτευξη ρεαλιστικών ή φυσικά ακριβών αποτελεσμάτων.
Τα νέα υλικά μπορούν να προστεθούν σε έναν υπάρχοντα φάκελο Smart Materials απλά κάνοντας κλικ στο μεγάλο εικονίδιο «+» στον πίνακα υλικού. Η μικρογραφία κάθε νέου υλικού δημιουργείται με βάση την εικόνα υφής που επιλέγετε για το κανάλι “Χρώμα” αυτού του υλικού.
Οι νέοι φάκελοι υλικού μπορούν να δημιουργηθούν ή να φορτωθούν πατώντας το μικρό “Κάτω βέλος” στην επάνω δεξιά γωνία του πίνακα υλικού και επιλέγοντας είτε τις επιλογές “Προσθήκη νέου φακέλου” ή “Προσθήκη υπάρχοντος φακέλου” .
Έξυπνο Υλικό RMB
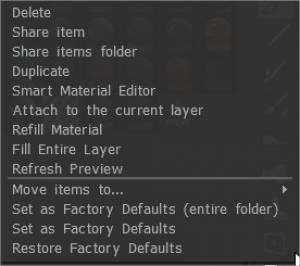
Διαγράφω:
Κοινή χρήση στοιχείου:
Κοινή χρήση φακέλου στοιχείων: Κοινή χρήση του φακέλου στοιχείων ως 3dcpack – αρχείο για κοινή χρήση με άλλους χρήστες.
Αντίγραφο:
Προσάρτηση στο τρέχον επίπεδο: Κάντε δεξί κλικ σε ένα Shader στον πίνακα. Επιλέξτε να προσαρτήσετε το τρέχον επίπεδο.
Υλικό αναπλήρωσης:
Γεμίστε ολόκληρο το πλέγμα:
Ανανέωση προεπισκόπησης:
Μετακίνηση αντικειμένων σε…:
Ορισμός ως εργοστασιακές προεπιλογές (Ολόκληρος ο φάκελος):
Ορισμός ως εργοστασιακή προεπιλογή:
Επαναφορά εργοστασιακής προεπιλογής:
Συνδέστε ένα έξυπνο υλικό σε ένα στρώμα (από την Digman)
Θα εμφανίσει ένα μικρό εικονίδιο στο στρώμα του υλικού Smart. Τώρα, εάν επιλέξετε ένα άλλο επίπεδο και επιλέξετε ξανά το επίπεδο με το προσαρτημένο Έξυπνο Υλικό, θα τονιστεί στον πίνακα Shaders. Μπορείτε να προσαρτήσετε μόνο ένα Shader ανά στρώμα.
Τοποθετήστε το ποντίκι σας πάνω από το εικονίδιο στο επίπεδο και θα εμφανιστεί μια μεγαλύτερη προεπισκόπηση. Δεν δίνεται όνομα, αλλά η προεπισκόπηση είναι αρκετά μεγάλη.
Μόλις προσαρτηθεί ένα Έξυπνο Υλικό στο επίπεδο, μπορείτε να το επεξεργαστείτε με το πρόγραμμα επεξεργασίας Smart Material και θα ενημερωθεί αυτόματα στο πλέγμα αφού αποθηκεύσετε το επεξεργασμένο Έξυπνο Υλικό. Δεν μπορείτε να εφαρμόσετε ξανά ένα Έξυπνο Υλικό στη θύρα προβολής με μη αυτόματο τρόπο χρησιμοποιώντας αυτήν τη μέθοδο, αλλά μπορείτε να αποσυνδέσετε και να προσαρτήσετε ξανά το Έξυπνο υλικό εάν χρειάζεται να το εφαρμόσετε ξανά.
Δεν μπορείτε να βάψετε χειροκίνητα σε ένα στρώμα με προσαρτημένο υλικό.
Φυσικά, αυτό θα απαιτούσε περισσότερα επίπεδα, αλλά είναι ένας τρόπος για να παρακολουθείτε τα Έξυπνα Υλικά σας μετά την εφαρμογή τους και εάν χρειάζονται επεξεργασία.
Τα παραπάνω είναι ένας καλός τρόπος δοκιμής Έξυπνων Υλικών και επεξεργασίας τους.
Παράδειγμα
Κάντε δεξί κλικ σε ένα Shader στον πίνακα. Επιλέξτε να προσαρτήσετε το τρέχον επίπεδο. Αποσυνδέστε ένα Έξυπνο Υλικό χρησιμοποιώντας την ίδια μέθοδο ή κάντε δεξί κλικ στο ίδιο το επίπεδο για την επιλογή αποσύνδεσης.
Μπορείτε να ονομάσετε επίπεδα με τρόπο ώστε να γνωρίζετε σε ποιο τμήμα του μοντέλου εφαρμόστηκαν.
Στη συνέχεια, έχετε έναν πλήρη τρόπο να γνωρίζετε ποιο μέρος του μοντέλου εργάζεστε και το υλικό Smart που είναι συνδεδεμένο σε αυτό.
Η αδιαφάνεια, η αδιαφάνεια βάθους και η αδιαφάνεια τραχύτητα πάνω από τα επίπεδα στον πίνακα επιπέδων εξακολουθούν να λειτουργούν.
Το «Attach to the current layer» του Smart Material από τον Yousung
Τρόπος χρήσης
1. Κάντε δεξί κλικ στο Έξυπνο Υλικό που θέλετε να χρησιμοποιήσετε
2. Κάντε κλικ στο «Επισύναψη στο τρέχον επίπεδο».
3. Μπορείτε να δείτε ότι το Έξυπνο Υλικό είναι προσαρτημένο στο επιλεγμένο επίπεδο.
* Τα προσαρτημένα έξυπνα υλικά λειτουργούν μεμονωμένα.
4. Εάν χρειάζεται να επεξεργαστείτε, κάντε δεξί κλικ στο επίπεδο και επεξεργαστείτε το στο Smart Material Editor.
5. Εάν πρέπει να αλλάξετε σε διαφορετικό υλικό, κάντε δεξί κλικ και χρησιμοποιήστε το ίδιο Επισύναψη στο τρέχον επίπεδο.
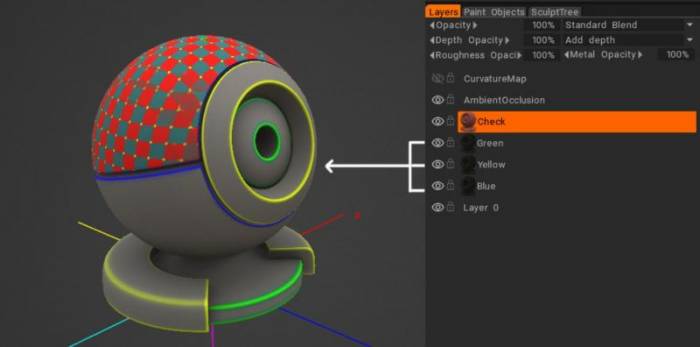
Όλα αυτά έχουν προσαρτημένο το ίδιο Έξυπνο Υλικό, αλλά το χρώμα έχει αλλάξει στο στρώμα.
Έξυπνο πρόγραμμα επεξεργασίας υλικών
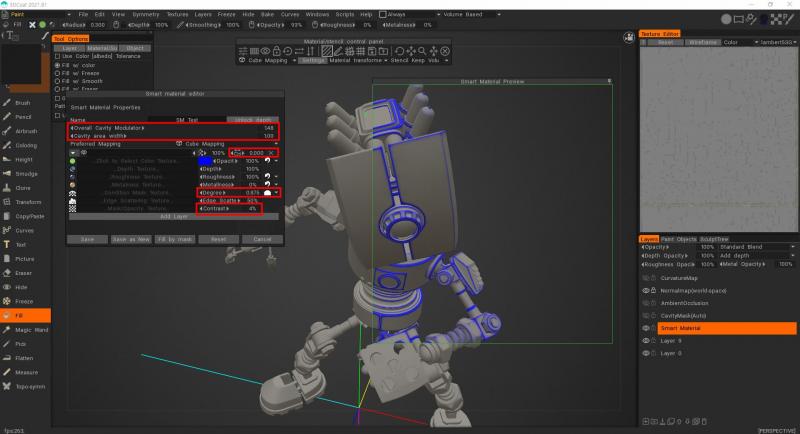
Όσα στρώματα θέλετε μπορείτε να δημιουργήσετε Έξυπνα Υλικά, επιτρέποντας αρκετά πολύπλοκα υλικά. Υπάρχει επίσης ένας αριθμός παραμέτρων για αυτά τα επίπεδα. Ας ρίξουμε μια ματιά σε αυτές τις Ιδιότητες Έξυπνου Υλικού τώρα.
Όνομα: Όνομα τρέχοντος υλικού.
Συνολική κλίμακα μετατόπισης:
Συνολικός διαμορφωτής κοιλότητας: Καθορίζει τη συνολική περιοχή επίδρασης για το υλικό.
Προτιμώμενη χαρτογράφηση: Χρησιμοποιήστε διάφορους τύπους mapping για να εφαρμόσετε το υλικό σας. Το Cube Mapping είναι ο προτεινόμενος τύπος mapping που χρησιμοποιείται με άνευ ραφής υφές.
Επίπεδο: Εκχωρήστε την ιεραρχία υφής σε επίπεδο ή δημιουργήστε νέα.
Χρώμα: Καθορίστε μια διάχυτη ή αλμπέντο υφή ή χρώμα.
Βάθος: Καθορίστε μια εικόνα σε κλίμακα του γκρι για βάθος. Το εικονίδιο του καναλιού βάθους στα Έξυπνα Υλικά μπορεί να φαίνεται σαν να είναι για Κανονικό Χάρτη, αλλά δεν είναι. Είναι αυστηρά για χάρτες μετατόπισης/ύψους σε κλίμακα του γκρι.
Γυαλάδα: Καθορίστε μια εικόνα σε κλίμακα του γκρι για γυαλάδα.
Μεταλλικότητα : Καθορίστε μια εικόνα σε κλίμακα του γκρι για τη μεταλλικότητα.
Μάσκα κατάστασης: Καθορίστε την περιοχή στην οποία εφαρμόζεται το στρώμα υλικού. Υπάρχουν διάφορες συνθήκες, οι οποίες παρατίθενται παρακάτω.
Edge Scattering: Καθορίστε με μια εικόνα πώς αντιμετωπίζονται τα άκρα της πάθησης.
Μάσκα: Μάσκες με εικόνα των περιοχών που καλύπτονται και δεν καλύπτονται.
Εάν παρέχετε έναν normal map για το Έξυπνο Υλικό, το 3DCoat θα προσφερθεί να το μετατρέψει στον χάρτη πρόσκρουσης επειδή τα υλικά απαιτούν πρόσκρουση. Αυτή είναι μια μη τετριμμένη λειτουργία, επομένως μπορεί να χρειαστεί λίγος χρόνος για τη μετατροπή για μεγάλους χάρτες.
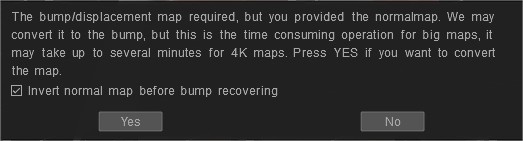
Γιατί το 3DCoat χρειάζεται βάθος; Επειδή μπορεί να βάψετε με διαφορετικά υλικά το ένα πάνω στο άλλο ακόμα και στην ίδια στρώση και το 3DCoat μπορεί να τα αναμίξει. Για να τα αναμίξετε 3DC χρειάζονται βάθος.
Από αυτό το βάθος σύνοψης δημιουργεί κανονικό χάρτη που βλέπετε ως την τελική απόδοση. Έτσι, εάν έχετε κανάλι βάθους, χρησιμοποιήστε βάθος για το έξυπνο υλικό.
Τα Έξυπνα Υλικά έχουν πολλές πτυχές στο 3DCoat. Υπάρχει η θύρα προβολής Σκίαση, Import/ Export χαρτών υφής Έξυπνου Υλικού και Έξυπνα Υλικά για τη ζωγραφική υλικών με φυσική ακρίβεια.
Προσαρμόστε τις παρακάτω επιλογές για να ελέγξετε την περιοχή ζωγραφικής χρησιμοποιώντας το CurvatureMap (από τον Yousung)
Ξεκινώντας από το 3DCoat 2021.53, η κοιλότητα RGB εισήχθη ως η προεπιλεγμένη μέθοδος υπολογισμού στο Texturing. Αυτό είναι ένα σημαντικό χαρακτηριστικό για το PBR Painting over the Texture/Mesh.
– Αρχικά, πρέπει να βεβαιωθείτε ότι είναι ενεργοποιημένη η έκδοση RGB cavity. Για να το κάνετε αυτό, μεταβείτε στην επιλογή Επεξεργασία > Προτιμήσεις, μεταβείτε στην ενότητα Εργαλεία και επιλέξτε Χρήση κοιλότητας RGB ως προεπιλεγμένη μέθοδο υπολογισμού κοιλότητας.
– Αφού ενεργοποιήσετε τη λειτουργία, μεταβείτε στο Μενού Υφή και επιλέξτε την επιλογή Υπολογισμός καμπυλότητας. Για να γίνει ο Υπολογισμός, πρέπει να περιμένετε λίγο.
– Τώρα μπορούμε να δούμε πώς ένας χάρτης κοιλότητας (RGB) εμφανίστηκε στα επίπεδα.
Εάν θέλετε να επεξεργαστείτε τον χάρτη Curvature στο Smart Material Editor
– Πρώτα, πρέπει να προσθέσετε τις συνθήκες στην τιμή του πτυχίου (περισσότερα σε κυρτό παράδειγμα) για να δείτε τις επιλογές “βάζο”.
– Εστιάστε σε ένα νέο εικονίδιο επεξεργασίας -μοιάζει με βάζο-, αυτό προστέθηκε και δεν υπήρχε πριν, και με τις άκρες περιστροφής διαμορφώνεται η λειτουργία ενημέρωσης. Είναι το πρόσθετο πλάτος κοιλότητας: Η τιμή 0 σημαίνει ότι η κοιλότητα λαμβάνεται από τις ρυθμίσεις υλικών ως έχουν.
Τιμές μικρότερες σημαίνουν πιο αιχμηρή κοιλότητα, περισσότερο από 0,5 – διεύρυνση της κοιλότητας. Ή, φυσικά, χρειάζεστε ένα στρώμα κοιλότητας RGB στη σκηνή για να αλλάξετε το πλάτος της κοιλότητας.
Λειτουργεί μόνο σε τέτοιες συνθήκες: περισσότερο σε κοίλο, περισσότερο σε κυρτό, λιγότερο σε κοίλο, λιγότερο σε κυρτό, περισσότερο σε επίπεδο και περισσότερο σε καμπύλο (μπορείτε να χρησιμοποιήσετε οποιαδήποτε από αυτές τις λειτουργίες).
– Η νέα παράμετρος είναι υπεύθυνη για την κοιλότητα της ακτίνας. Επηρεάζεται επίσης από τις ρυθμίσεις βαθμού και αντίθεσης.
– Συνολικός διαμορφωτής κοιλότητας
– Πλάτος περιοχής κοιλότητας
– Πρόσθετο πλάτος κοιλότητας
– Βαθμός
– Αντίθεση
Η χρήση της κοιλότητας RGB στο 3DCoat 2021
Συνθήκες (Περιοριστής ύψους/χρώμα)
Συνθήκες Ύψους/Χρώμα περιοριστή
Επιλέξτε πώς το βάθος, το χρώμα και η στιλπνότητα των πινελιών σας επηρεάζονται από τα χρώματα, το ύψος και άλλες παραμέτρους. Θυμηθείτε να το ορίσετε σε “Καμία” όταν ολοκληρώσετε τη χρήση αυτής της επιλογής.
Μπορείτε να προσπελάσετε τις συνθήκες κάνοντας κλικ στο εικονίδιο δίπλα στο επίπεδο Μάσκα συνθήκης (και δίπλα στο Πτυχίο). Αυτό δίνει ακόμη μεγαλύτερη πρόσβαση σε διάφορους τρόπους εφαρμογής του στρώματος υλικού σας.
Οι προϋποθέσεις αυτές είναι:
Πάντα: Ισχύει για κάθε pixel του στρώματος.
Περισσότερα για το Concave: Αυτό ισχύει για περιοχές που είναι πιο κοίλες και σας επιτρέπουν να γεμίσετε ρωγμές.
Περισσότερα για το Convex: Εφαρμόζεται σε πιο κυρτές περιοχές, εφαρμόζοντας το υλικό σε πιο στρογγυλεμένες εξωτερικές επιφάνειες.
Less on Concave: Παρόμοιο με το More on Concave, αλλά ισχύει στην αντίθετη μορφή επιτρέποντας λίγο λιγότερο στις κοίλες περιοχές και λίγο περισσότερο στις κυρτές περιοχές.
Less on Convex: Παρόμοιο με το More on Convex, αλλά ισχύει στην αντίθετη μορφή επιτρέποντας λίγο λιγότερο στις κυρτές περιοχές και λίγο περισσότερο στις κοίλες.
Περισσότερα για Επίπεδες: Εφαρμόζεται μόνο σε πιο επίπεδες επιφάνειες.
Περισσότερα για το Curve: Αυτό ισχύει μόνο για πιο καμπύλες επιφάνειες.
Περισσότερα για το Lit: Ισχύει για περιοχές που είναι καλά φωτισμένες και χρησιμοποιεί έναν χάρτη απόφραξης περιβάλλοντος για τον προσδιορισμό της τοποθέτησης.
Περισσότερα στο Shadow: Παρόμοιο με το More on Lit, αλλά ισχύει για τις πιο σκοτεινές περιοχές ενός χάρτη Ambient Occlusion.
Περισσότερα στην κορυφή: Εφαρμόζεται μόνο στις επάνω περιοχές της επιφάνειας.
Περισσότερα για το κάτω μέρος: Εφαρμόζεται μόνο στις κάτω περιοχές της επιφάνειας.
Περισσότερα για τα πλαϊνά: Εφαρμόζεται μόνο στα πλαϊνά της επιφάνειας.
Προϋποθέσεις : Αυτό το βίντεο δείχνει τη χρήση των Συνθηκών για την εφαρμογή βαφής σύμφωνα με προκαθορισμένους περιορισμούς, όπως περιοχές κοιλότητας/εσοχής, άκρες/προεξοχές, επίπεδες, κυρτές, φωτισμένες, σκιές κ.λπ.
Απόδοση φυσικής βάσης
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες για το PBR μπορείτε να βρείτε στους ακόλουθους πόρους:
https://www.marmoset.co/toolbag/learn/pbr-practice
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1Fb9_KgCo0noxROKN4iT8ntTbx913e-t4Wc2nMRWPzNk/edit
Επιλογές προεπισκόπησης στένσιλ και έξυπνου υλικού
Επιλογές προεπισκόπησης
Όταν ενεργοποιείτε ένα από τα Στένσιλ Υλικών ή και τα δύο ταυτόχρονα, θα έχετε ένα νέο πλαίσιο στην οθόνη.
Αυτό το πλαίσιο περιέχει όλες τις επεξεργάσιμες λειτουργίες τόσο για Έξυπνα Υλικά όσο και για Στένσιλ.
Προσθέστε πολλές εικόνες σε έναν νέο φάκελο.
– Τι γίνεται αν έχω κάποιο σύνολο εικόνων όπως αυτό στην εικόνα; Υπάρχει τρόπος να τα ρυθμίσετε σε μια δομή φακέλου που να μπορεί να import το 3DCoat ; Είναι μόνο εικόνες Albedo για ζωγραφική προβολής.
Στον πίνακα Smart Material, επιλέξτε Create New Folder και, στη συνέχεια, πατήστε το εικονίδιο 3 κουκκίδων.
Επιλέξτε την επιλογή: προσθέστε έναν υπάρχοντα φάκελο.
Πλοηγηθείτε μέσα στο περιεχόμενο του φακέλου και επιλέξτε μόνο την πρώτη φωτογραφία. Πατήστε άνοιγμα.
Προσθήκη υπάρχοντος φακέλου υλικών.
Προσθέστε τα Έξυπνα υλικά από έναν υπάρχοντα φάκελο. Θα δημιουργηθεί ένας νέος φάκελος Υλικά με το ίδιο όνομα. Επιλέξτε τουλάχιστον ένα αρχείο για να προσθέσετε αυτόματα όλα τα αρχεία από το φάκελο στη λίστα.
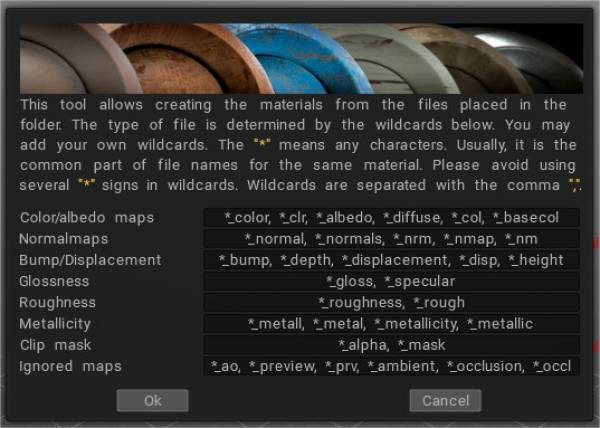
Αυτή είναι η πλήρης λίστα των ψευδωνύμων (στο τέλος του ονόματος αρχείου) που χρησιμοποιούνται για την αναγνώριση της χρήσης υφής:
Χτύπημα:
_DEPTH, _BUMP, _DEEP, _DISPL, _DISP, _DISPLACEMENT, _D
Κανονικός χάρτης:
_NMAP, _NM, _NORMAL, _NORMALMAP, _NORM, _NORMALS, _N
Χρώμα:
_COLOR, _CLR, _DIFFUSE, _ALBEDO, _CL, _RGB, _DIF, _C
Στιλπνότητα:
_SPEC, _GLOSS, _GLOSNESS, _GLOSINESS, _GLOSSNESS, _GLOSSINESS
Τραχύτητα:
_ΤΡΑΧΙΑ, _ΤΡΑΧΙΑ, _Ρ
Κλιπ μάσκας:
_MASK, _MSK, _MS, _CLIP, _ALPHA
Μεταλλικότητα:
_MET, _METAL, _METALL, _METALLICY, _METALICITY, _METALNESS, _METALLNESS, _MT, _ME, _METL
Αγνοήθηκε:
_PREVIEW, _PREV, _TMB, _THUMBNAIL, _PRV, _AO, _OCCLUSION
Το οποιοδήποτε από . – Το ~ μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί αντί για το σύμβολο _.
Εάν κάποιος χάρτης ονομάζεται με ένα κενό στο όνομα, η υφή εκχωρείται ως νέο Έξυπνο Υλικό. Επεξεργασία
Φροντιστήρια
PBR Smart Materials : Αυτό είναι απλώς ένα γρήγορο βίντεο που έφτιαξα και δείχνει μερικά από τα νέα και εκπληκτικά υλικά PBR της 3D-Coat. Μπορείτε να δημιουργήσετε όλα τα νέα υλικά από την αρχή, αλλά συνοδεύεται από ένα σωρό προκατασκευασμένα και έχουν πολλές λειτουργίες που μπορείτε να προσαρμόσετε για να αλλάξετε την εμφάνισή του. Του Φιλ Νόλαν.
Σύνδεσμοι με ορισμένα αξιόλογα στοιχεία τρίτων μερών .
Βελτιωμένη μηχανή Brush και μικρογραφίες επίπεδων υλικών
PBR (Smart) Materials από τον Phil Nolan: Αυτό είναι απλώς ένα γρήγορο βίντεο που έφτιαξα και δείχνει μερικά από τα νέα και εκπληκτικά υλικά PBR της 3DCoat. Μπορείτε να δημιουργήσετε όλα τα νέα υλικά από την αρχή, αλλά συνοδεύεται από ένα σωρό προκατασκευασμένα και έχουν πολλές λειτουργίες που μπορείτε να προσαρμόσετε για να αλλάξετε την εμφάνισή του.
Misted glass : Βίντεο διαδικασία ομίχλης γυαλιού σε πραγματικό χρόνο από τον Roman Makarenko.
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά  English
English Українська
Українська Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Português
Português Italiano
Italiano Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 (台灣)
中文 (台灣) Dansk
Dansk Slovenčina
Slovenčina Türkçe
Türkçe Nederlands
Nederlands Magyar
Magyar ไทย
ไทย हिन्दी
हिन्दी Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Eesti
Eesti Čeština
Čeština Română
Română Norsk Bokmål
Norsk Bokmål