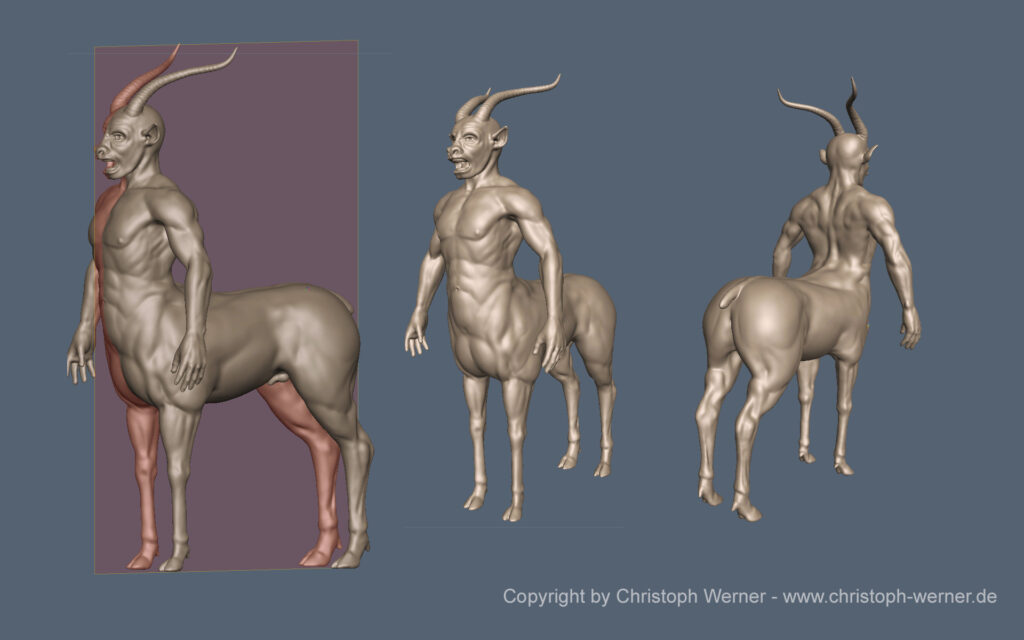
3DCoat Autopo test session By Christoph Werner
Hello friends.
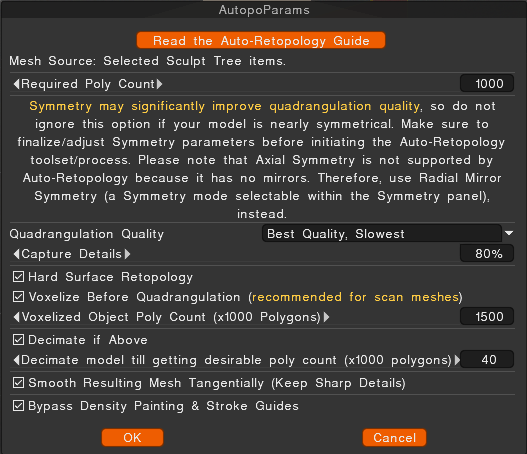
I took some hours to prepare a big autopo test for 3DCoats last Autopo routine update. It was a lot of work to make all the tests and get a good settings result. But it was worth the time.
I have made more than 20 calculations! In the gallery you will find the very best settings I worked out in my tests.
So you may save a lot of time for your own work and just take the setting you think you need. Of course there are more ways to test, but I think my results are good for the most situations.
All tests were done without guide lines or density areas.
The basic rules for using Autopo in 3DCoat
- If your model is symmetrical then switch scene symmetry ON. It increases the Autopo quality result a lot.
- Start with small values for Capture Details and Decimate if Above. The most scenes don’t need more than a value of 50 in both options.
- The higher the Capture Details value, the more poly stars can appear in the Autopo mesh.
- The higher the Decimate if Above value, the more render time is used.
- Switching Voxelise Before Quadrangulation to OFF leads often to better quality. If you have snapping problems in the autopo mesh, then switch it ON.
- Try not to use Voxelise Before Quadrangulation value higher than 50% of your whole template model poly amount.
Example: A sculpt model with 2.000.000 polys needs a value of “1.000”. (1000 x 1000=1.000.000=50% of 2 M.) - To disable the Decimate if Above option can lead to very long render times.
(3D Coat is not crashed. You just need a lot of patience… It could result in an hour and more.) - Hardsurface retopology Crease Angle: I have not tested it in detail. But my test experience resulted in ignoring this value. If you have hints where this option is good to have, drop me a line here please.
- Smooth Resulting Mesh Tangentially can be set ON.
Density
When using density just mark the areas that have to be created with more polygons. The value describes the target amount of polygins in this areas. A value of 2 will lead to a double amount of the actually created polygons.
Don’t forget: Density will always “move” polygons from one area to increase another. So you will have less polygons at some model parts.
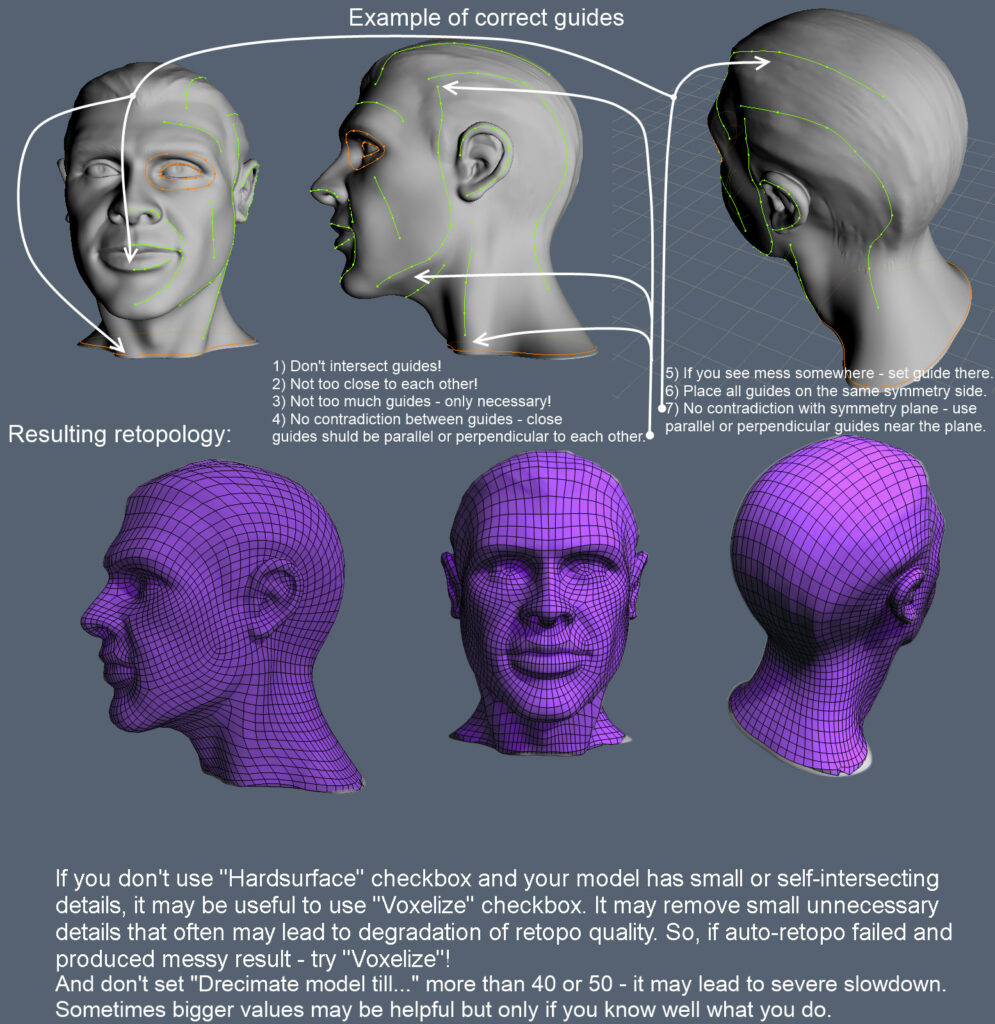
Guide lines
Hand painted guide lines help the Autopo routine to distribute the right polyflow. 3DCoat will try to follow your settings but this is only a approximation. There are some rules before using guide lines. Wrong usage can results in mesh problems.
- Set less guide lines.
- Don’t set lines too tight. Keep enough room inbetween.
- Try to use rings at areas like eyes or similar.
- Don’t cross lines.
The following official documentation image describes it well:

Test results with ratings for my settings
The more stars I gave the better the autopo result was. The result depends on the type of model used for retopology, for which there is no fixed guide.
Everything translates to trial and error for each circumstance.
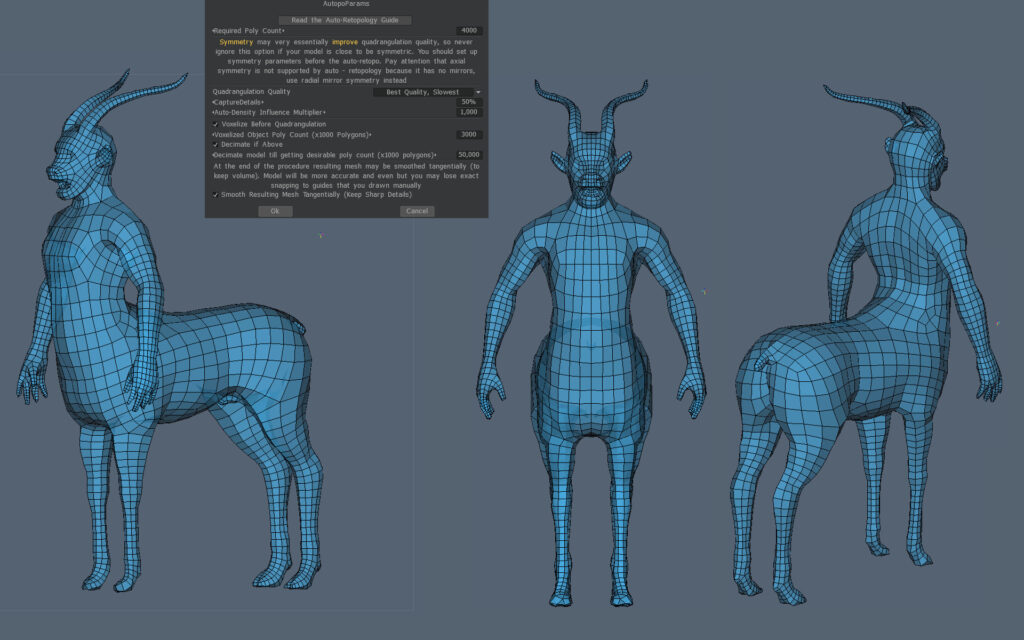
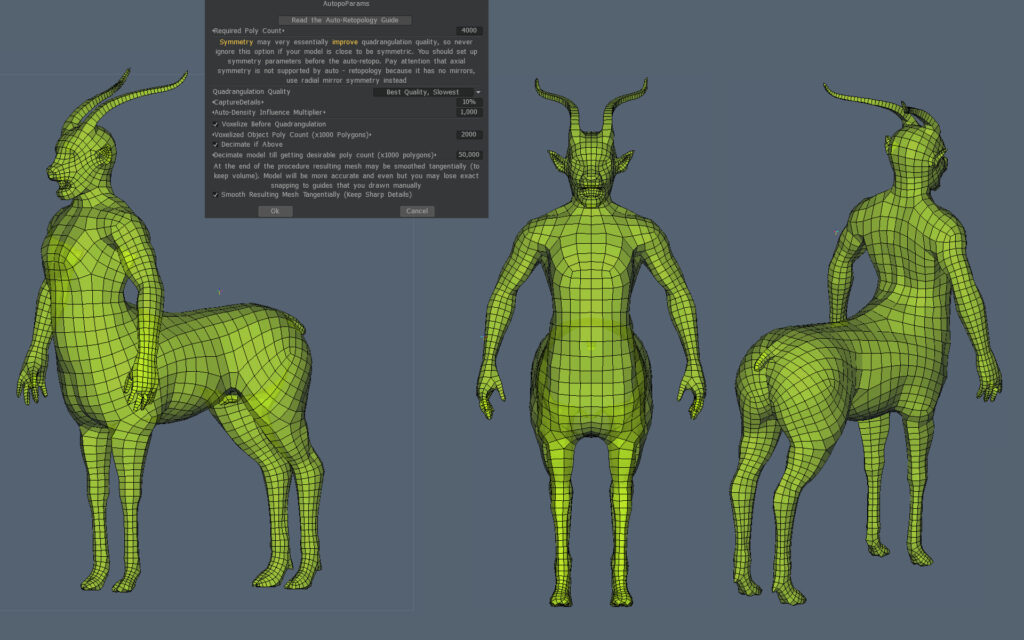
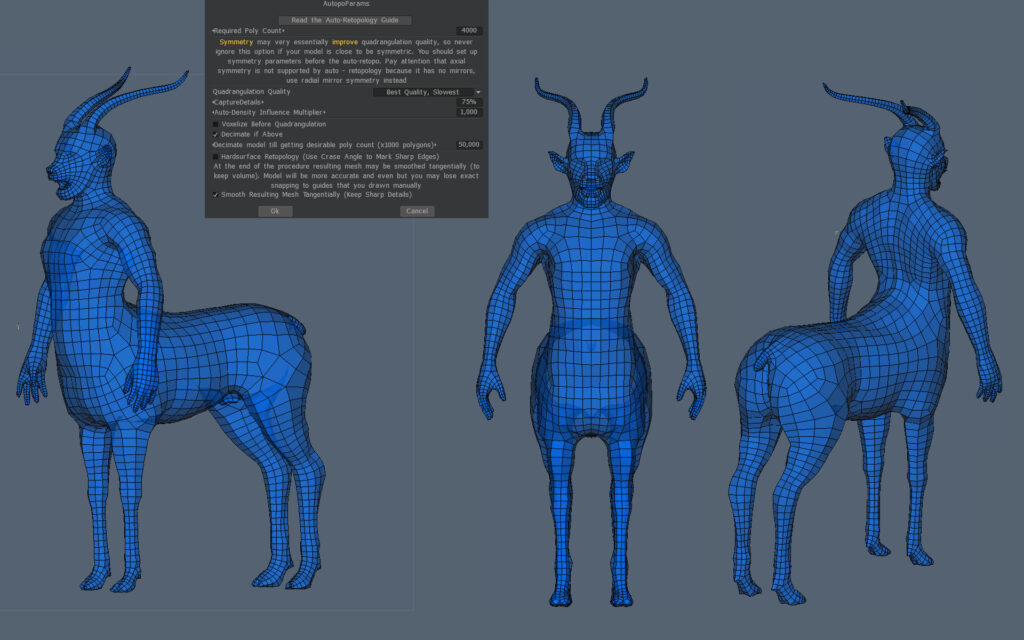
Testing settings for Hard Surface models
Autopo, or automatic retopology, for hard surface models is the process of automatically converting a high-polygon, inorganic model into a clean, low-polygon mesh with all-quad topology. While traditionally difficult for automated algorithms, modern software offers specialized features to produce a clean, usable mesh that respects the model’s sharp edges and flat planes.
This workflow is crucial for optimizing models for video games and other real-time applications, where performance is critical. It allows artists to create complex, high-detail concepts without worrying about topology, then automatically generate a simplified, animation-ready version later.
How hard surface auto-retopology works
Standard automatic retopology tools prioritize an even distribution of polygons, which works well for smooth, organic surfaces. Hard surface models, with their distinct angles and precise shapes, require a more advanced approach. Modern auto-retopology algorithms address this by:
- Edge detection: The software analyzes the mesh’s curvature to identify sharp edges, rather than relying on a simple crease angle. This allows it to preserve the hard edges of the model.
User guidance: Many tools allow artists to add “stroke guides” or “density painting” to direct the algorithm. This gives manual control over areas where specific edge loops are critical for function or detail.
Parameter adjustment: Specific settings can be tweaked to favor hard surface models. In Maya, for instance, high “Topology Regularity” and “Face Uniformity” values can be used to convert a mesh into quads while preserving hard edges.
Limitations and workflow tips
Hard surface autopo is a hard task whose result depends on the complexity of the model.
- Not perfect: While automated tools have become extremely powerful, they rarely produce a perfect mesh for complex models, especially for animation. Some manual cleanup is almost always required.
- Clean source mesh: Ensure your high-poly sculpt is free of errors, such as non-manifold edges or overlapping vertices, as these can cause problems for the auto-retopology algorithm.
- Separate parts: For very complex models with distinct, connected parts, better results can be achieved by separating the objects into individual components before running the auto-retopology routine.
- Baking details: Following retopology, high-frequency details from the original model are “baked” into a normal map. This allows the low-poly mesh to retain the appearance of the original’s surface complexity
 Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai  English
English Українська
Українська Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Português
Português Italiano
Italiano Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 (台灣)
中文 (台灣) Dansk
Dansk Slovenčina
Slovenčina Türkçe
Türkçe Nederlands
Nederlands Magyar
Magyar ไทย
ไทย हिन्दी
हिन्दी Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Eesti
Eesti Čeština
Čeština Română
Română Norsk Bokmål
Norsk Bokmål