The model to be used seamlessly over the spline should consist of 3 objects, named as Top, Bottom, and Middle.
The Middle object is the one that will be constantly tiled along the curve.
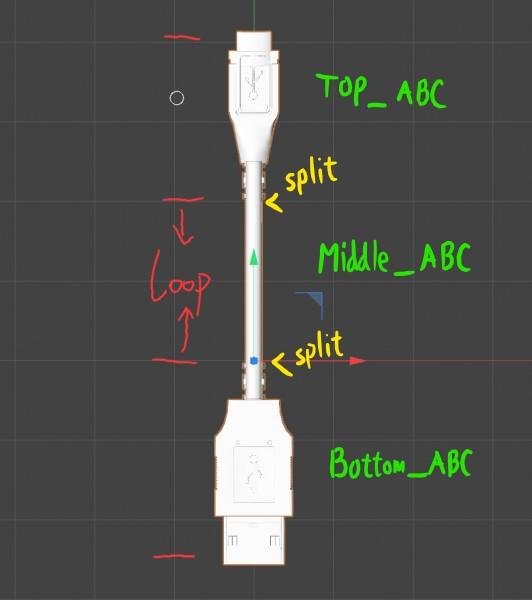
It has vertices approximately in the range [0..1] along Y-axis.
Look at the loop part. To create a spline model with three parts LOOP must begin at 0,0,0 Global Space coordinates.

Top and bottom of the Middle object should be open and opposite vertices positions should differ exactly by 1 along Y.
Here’s an example of the Middle object:
There may be several objects named “Middle_anything”. They should get identical open edges, but in the middle the geometry may be different. 3DCoat will use random middle objects to place them along the curve.
The Top object is placed exactly over the Middle object and has an approximate [1..2] range of Y-coordinate. This object is open at the bottom, the vertices should get exactly the same values as on the Middle top vertices.
An example of the Top object, marked red:
The Bottom object is placed exactly under the Middle object and has an approximate [-1..0] range of Y-coordinate. This object is open at the top, the vertices should get exactly the same values as on the Middle bottom vertices.
Here’s an example of the Bottom object, marked red:
The whole curve will be tiled with Middle sections, the first section is Bottom, the last one is Top.
If the curve is closed, only the Middle sections will be used.
Open edges will be welded with nearby sections, so if you made everything correctly, the whole object will be closed.
So, the final model looks like this:
And this is how it looks in 3DCoat
If the middle part of the model does not repeat, check the following
1. Is the object named as follows?
– Top_@@@
– Middle_@@@
– Bottom_@@@
2. Is the connection part of the object ‘Open edge’?
– Spline guidelines say that the top-middle-bottom part should be an open edge
3. This is just in case, but have you actually registered and tested it instead of a preview in the creation stage?
– It does not seem to be repeated in the preview, but if you follow steps 1 and 2 properly, the result will be repeated middle-parts normally.
 Français
Français  English
English Українська
Українська Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Português
Português Italiano
Italiano Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 (台灣)
中文 (台灣) Dansk
Dansk Slovenčina
Slovenčina Türkçe
Türkçe Nederlands
Nederlands Magyar
Magyar ไทย
ไทย हिन्दी
हिन्दी Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Eesti
Eesti Čeština
Čeština Română
Română Norsk Bokmål
Norsk Bokmål