A render comparison of different roughness values in 3DCoat and Blender by DMG
I was going between 3DC and Blender a bit trying to hit the sweet spot I wanted for something, and I noticed differences between the two renders, especially caused by varying roughness values.
I decided to get a bit scientific about it, so here’s the results of my tinkering. I used the studio.exr panorama from Blender in both programs for a fair comparison. The 3DCoat environment settings were left at default, but the light was deactivated. The HDRI was normalized when I imported it. The HDRI strength was left at default value in Blender too.
A simple sphere, identical color value in all renders.
I’m making no judgement as to which renderer is ‘better’. This is just purely for comparison, to see how roughness values appear in each in order to make texturing a bit more predictable.
I did notice that in the HDRI there is a tiny but bright spotlight high up adjacent to the other light, but for some reason this isn’t picked up in the 3DCoat renders. Perhaps it’s just a tiny pinprick and too small to be picked up. I don’t know. There also appears to be a light down low, right of center, but only on the renders for 25% to 40% roughness in the 3DCoat renders. I don’t know where that’s coming from. It isn’t apparent in any of the others.
The rows are: 3DCoat’s GGX, Handpaint, Render; then Blender’s Eevee, Cycles.
* I think the Handpaint render (compared to the GGX one) has slightly lower intensity in the bright highlights, as well as ever so slightly more diffuse reflections when the roughness reached mid-levels. And compared to the 3DCoat render, the bright highlights in the Handpaint render are a touch more intense, and as with the GGX ones, much more defined.
Looking at the Handpaint renders and the Blender Cycles renders, they’re actually very similar. This is excellent.
I feel that if I use the Handpaint preview, I will be seeing a very close approximation of what I’ll get in Blender. So my chart is now redundant, based on the reason I created it in the first place, but it has nevertheless been very useful.
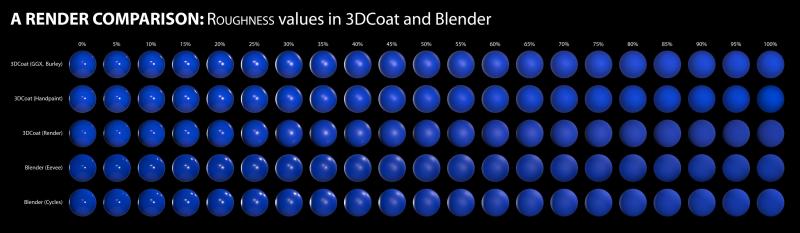
The most noticeable differences is that the reflections in the 3DCoat Paint Room preview are a touch more intense than both of Blender’s renders, but the same reflections are a bit feinter in 3DCoat’s Renderer.
Also, at around 35-40% roughness, the 3DCoat Renderer has greater blur on the main reflections near the center, which has almost become a single bright patch, whereas all the others still have two distinct light sources.
Like I said, this isn’t about picking a ‘winner’ or ‘favorite’. It’s just to help me predict how my textured objects will appear and render in Blender to save time to-ing and fro-ing making adjustments.
 Deutsch
Deutsch  English
English Українська
Українська Español
Español Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Português
Português Italiano
Italiano Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 (台灣)
中文 (台灣) Dansk
Dansk Slovenčina
Slovenčina Türkçe
Türkçe Nederlands
Nederlands Magyar
Magyar ไทย
ไทย हिन्दी
हिन्दी Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Eesti
Eesti Čeština
Čeština Română
Română Norsk Bokmål
Norsk Bokmål