Let we have mesh like on example. This is pictured schematically as side view, objects to be baked are
grey and blue, red is retopo mesh.
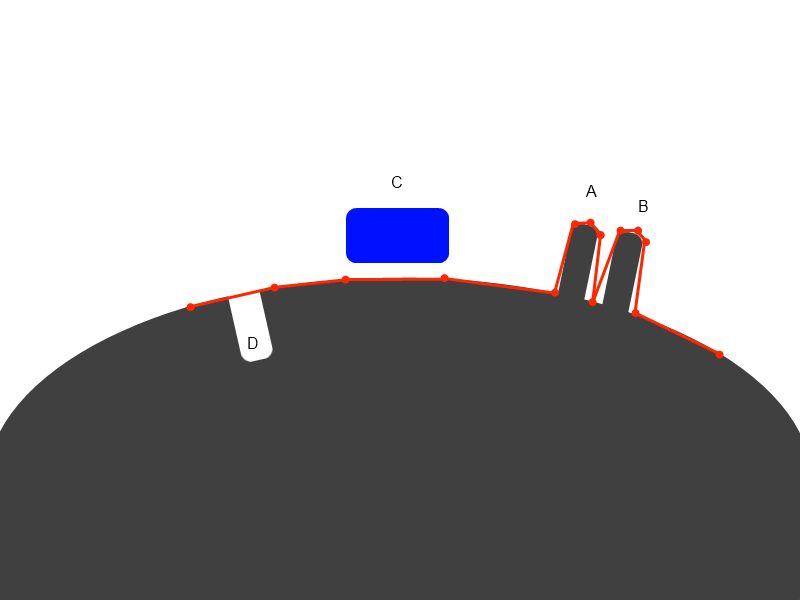
If you will try to bake in retopo room using Retopo->Bake with NM (to get normalmap) you will see the
dialog:
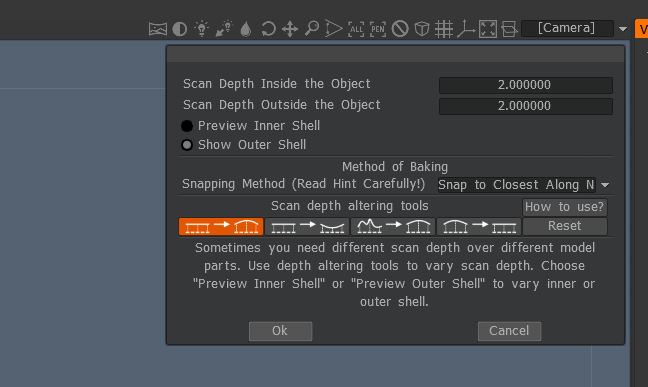
Let us look on settings. The principle of baking is scanning along retopo mesh normal to get to the baked
object surface. Later we will describe several approaches for this purpose.
Scan depth settings are well understood from this picture:
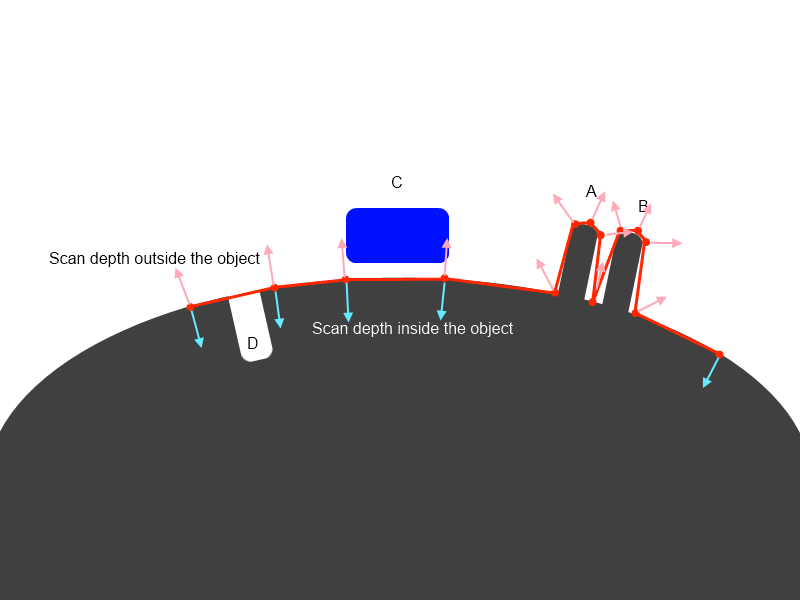
It are lengths or rays that follow normal direction. The longer rays, the more distant objects will be
taken into account. But if you will make it too long A and B will be baked incorrectly, if you will set it too
short, C and D will not be captured. We will describe later how to solve such problems in 3D-Coat. Let us
continue options discovering.
There are 2 methods of baking
1) Snap to closest along normal:
It is simplest approach that will work well in simple cases. It is default mode. In this case the point
closest to the retopo mesh will be baked. You may set bigger scan depth for this method and it still will
work. In our example you may set it twice longer and it will correctly capture details A, B, D. But C will
not be captured at all because grey surface is closest to the retopo mesh.
2) Snap to outer surface:
This method is intended for complex cases and rather pro users. It captures most distant details in
normal direction. Let us look on our example. If we will set outer scan distance twice longer then C will
be correctly baked, but A and B will not because of most outer will be neighbor spike and you will get
mess on normalmap. So you should not set big scan distance for this method. But if you will set it too
small so that A and B will be captured, C will not be captured.
For this purpose “Scan depth altering tools” introduced. Use the tools to alter scan depth, separately for
outer and inner shells of scanning depth. Grow, decrease, smooth or erase field. Use CTRL to invert
action and SHIFT to smooth field.
There are several additional tips for baking:
- If you made not successful pass of baking and want to try it again, delete object that was add during
baking process in paint room using Objects palette. Usually it is last object in Objects palette (Windows-Popups->Objects). - If you like result and want to export lowpoly mesh and textures – delete your reference objects (hide voxel objects or delete paint object) and export from paint room using File->Export or Textures->Export.
- It is convenient to hide reference objects after baking to estimate result. Use VoxTree to hide voxels and Objects to hide paint and reference objects. Don’t forget to turn it on again if you want to bake them again!
- It is much better to use Retopo->Bake with NM / Bake into scene (microverts) / Bake with Ptex instead of using Retopo->Texture baking tool because of much better flexibility.
- If you are baking for microverts/ptex to get displacement and can’t get good result because of spikes in just several single points, use Layers->Clamp depth of the layer to cut off problematic spikes.
- If you retopo each voxel layer separately you will get set of intersecting retopo layers. It usually happens if you are using Autopo. It is problematic to bake all that straightforward. If you have same names for retopo and voxel layers use Retopo->Use names correspondence for baking.
You may also check if all is correct using Retopo->Check groups and volumes correspondence. - If you have huge reference mesh 5-100 M don’t try to import it as reference mesh, it will fail anyway. Use File->Import for vertex painting instead. It will work much better. You may use startup screen options.
- It is better to avoid sharp angles between faces (like in example, retopo mesh between A and B), even angle a little less 90 degrees are not recommended, it will lead to problems if you are using 3DCoat’s method for calculating normals (Edit->Preferences->Normals calculation).
Maya normals calculation method will work correctly in this case, so if you need sharp angles, use Maya normals calculation in Preferences.
This is related to method of calculation. 3DCoat calculates normals as weighted average of neighbor faces, weight is proportional to face square. It allows to display bevel between faces correctly.
But if there is sharp angle between big and small faces then vertex normal will be negative to small face normal and baking on that face will fail. Maya’s method calculates vertex normal as arithmetical average of neighbor faces normals. It is more appropriate for baking, but not good to display meshes without normalmap.
Generally we recommend to add bevel between sharp edges.
 Italiano
Italiano  English
English Українська
Українська Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Português
Português Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 (台灣)
中文 (台灣) Dansk
Dansk Slovenčina
Slovenčina Türkçe
Türkçe Nederlands
Nederlands Magyar
Magyar ไทย
ไทย हिन्दी
हिन्दी Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Eesti
Eesti Čeština
Čeština Română
Română Norsk Bokmål
Norsk Bokmål