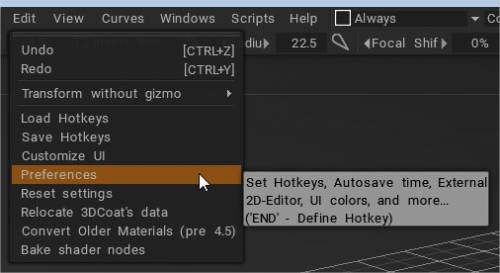
Ця панель відкриває детальне діалогове вікно параметрів, які дозволяють налаштувати 3DCoat. Ми надамо вам загальний огляд категорій і доступних варіантів.
Вкладка Загальне
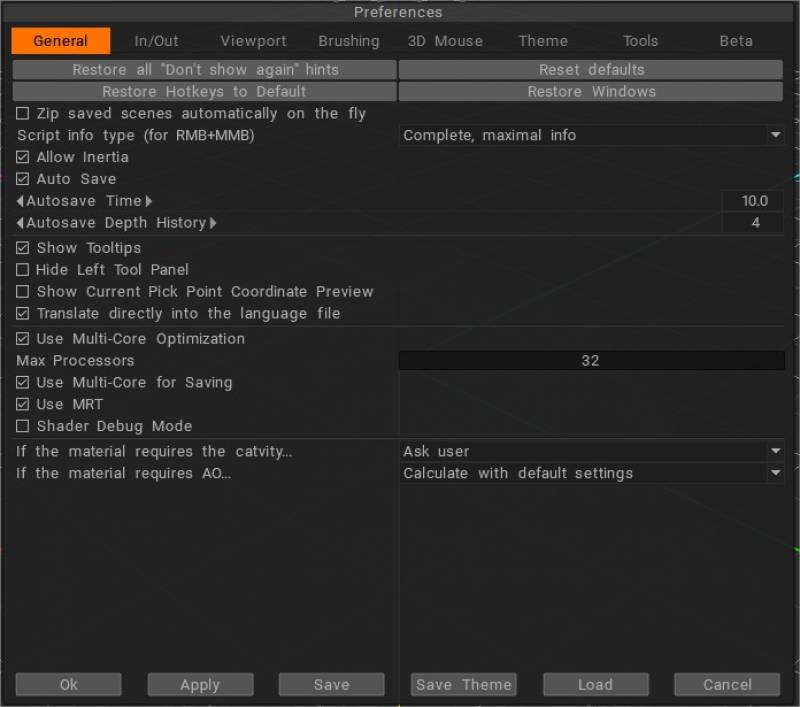
У верхній частині цього діалогового вікна є чотири постійні параметри, які дозволяють повернути 3DCoat до «заводських» налаштувань за замовчуванням:
Відновити всі підказки «Більше не показувати»: укажіть, які підказки ви бажаєте відображати та де їх відображати.
Скинути гарячі клавіші: відновити всі налаштування до стандартного стану.
Відновити гарячі клавіші до стандартних: скинути гарячі клавіші до стану, у якому вони були розповсюджені.
Відновити вікна та їх розташування: відновити положення та розмір усіх вікон за замовчуванням.
Zip збережені сцени:
Дозволити інерцію : дозволяє використовувати колесо прокручування, щоб пришвидшити прокручування інструментів і діалогових вікон так само, як колесо прокрутки працює, наприклад, у веб-браузері.
Автозбереження : увімкніть/вимкніть автозбереження та встановіть час автозбереження , щоб налаштувати часові інтервали та історію глибини. Файл автозбереження має назву autosave.3b, який знаходиться в папці User Data.
Історія глибини автозбереження: кількість файлів автозбереження, які будуть зберігатися послідовно.
Показати спливаючі підказки: дозволяє показувати або приховувати спливаючі підказки біля курсора миші .
Показати розгорнуті підказки (внизу тривимірного вікна перегляду) .
Приховати ліву панель інструментів: ви можете приховати ліві панелі інструментів, якщо бажаєте використовувати меню «пробіл».
Показати попередній перегляд поточних координат точки вибору .
Використовуйте багатоядерну оптимізацію: установіть свої параметри відповідно до апаратного забезпечення вашої системи.
Максимальна кількість процесорів: кількість процесорів для використання з 3DCoat.
Використовуйте Multi-Core для збереження .
Використовуйте MRT: використовуйте кілька цілей візуалізації, щоб прискорити normal map в реальному часі.
Режим налагодження шейдерів: режим налагодження шейдерів дозволяє бачити помилки під час компіляції шейдерів. За замовчуванням вимкнено.
Нові параметри в параметрах для шарів AO/Curvature: обчислювати значення за замовчуванням/запитувати за допомогою діалогового вікна/пропускати обчислення.
Import та Export
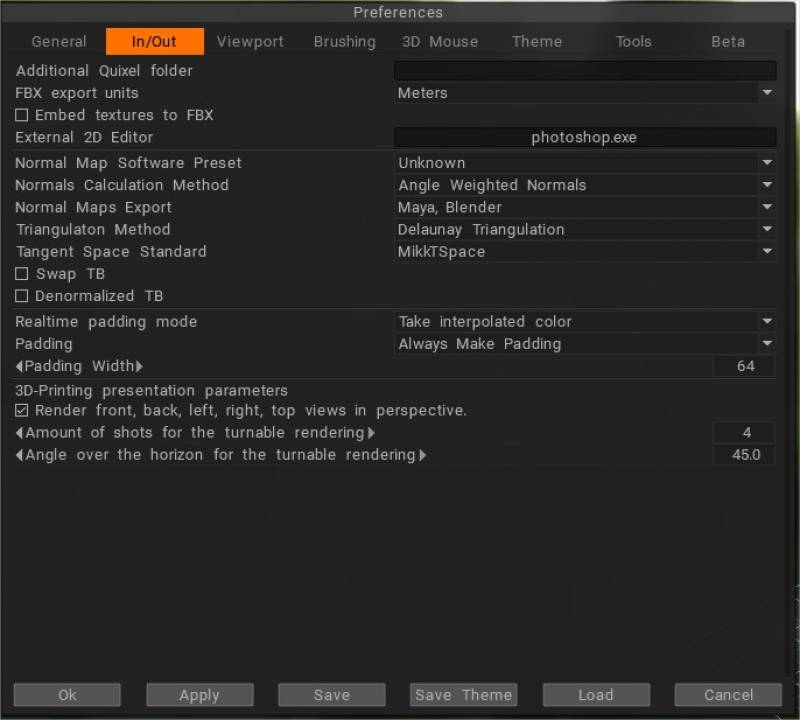
— Покращення підтримки Megascans: нова опція «Правка» > «Параметри» > «Введення/виведення» > «Додаткова папка Quixel».
Під час запуску «3DCoat» перевіряє «Завантаження» та «Додаткову папку Quixel» на наявність нових матеріалів Quixel у вигляді zip-архівів і вже видобутих папок.
Одиниці export FBX: значення одиниць у FBX. Метри означають масштаб 1:100, Сантиметри – 1:1, Міліметри – 10:1. Це стосується лише export FBX.
Вставити текстури у FBX: під час export FBX текстури буде вбудовано безпосередньо у файл FBX.
Зовнішній 2D-редактор: цей шлях використовуватиметься для визначення того, яку зовнішню програму «Paint» ви бажаєте використовувати (наприклад, Photoshop) для редагування 2D-зображень. Цей редактор повинен мати можливість редагувати файли PSD, тому зазвичай це Adobe Photoshop. Цей редактор буде називатися «Редагувати»-«Синхронізувати шари з Ext. Редагувати/Редагувати всі шари в Ext. Редагувати/Редагувати проекції в Ext. Редактор».
Попередні налаштування програмного забезпечення «Звичайні карти». Використовуйте цей набір параметрів, щоб точно вказати, як ви бажаєте працювати з вашими звичайними картами, внутрішніми та зовнішніми, у програмах сторонніх розробників. Для кожного програмного забезпечення є список запропонованих параметрів.
Метод розрахунку нормалей: виберіть спосіб розрахунку нормалей сітки для малювання.
export звичайних карт: виберіть стандарт експорту звичайних карт: 3D-Max або Maya.
Метод тріангуляції: метод тріангуляції важливий для сумісності карт нормалей. Якщо метод тріангуляції не відповідає вашому програмному забезпеченню моделювання, і ви bake карти нормалей, на квадрациклах можуть з’явитися хрестоподібні артефакти.
Стандарт дотичного простору: дотичний простір важливий для правильного відтворення карт нормалей. Якщо ви використовуєте неправильний дотичний простір, шви будуть видимі на запеченій моделі у вашому програмному забезпеченні для моделювання. Отже, після експорту з 3DCoat вам потрібно вибрати метод, який добре сумісний із вашим програмним забезпеченням для моделювання. Різниця не надто помітна на органічних моделях, але може істотно вплинути на випікання моделей з твердою поверхнею.
Swap TB: інвертувати нормальний напрямок.
Денормалізований TB: Денормалізоване Baking текстур означає скидання довжини кожної нормалі на карті до 1.
Режим заповнення в реальному часі: існує кілька методів заповнення.
– Перший лінійно інтерполює колір між пікселями з протилежного острова.
– Другий бере найближчий піксель з протилежного острова.
– Третій, наївний, бере найближчий піксель з поточного острова.
Заповнення: коли ви export текстури, вас запитають, чи потрібна рамка навколо кластерів текстур (заповнення). Цей параметр дозволяє автоматично відповісти на запитання.
Ширина відступу: ширина відступу використовується під час експорту текстури.
Параметри презентації 3D-друку
Вигляд спереду, ззаду, ліворуч, праворуч і зверху в перспективі.
Кількість кадрів для візуалізації вертушки.
Кут над горизонтом для візуалізації вертушки.
Видове вікно
Система координат Z-up: система координат на основі Z-up для сумісності з Rhino, 3DS-Max та іншими програмами з віссю Z up.
Використовувати фіксований масштаб сцени: якщо ви використовуєте фіксований масштаб сцени, об’єкт завжди відкриватиметься в цьому масштабі, за винятком сцен, збережених раніше. Це може бути проблематично у випадках, коли об’єкти занадто великі або занадто малі. Рекомендується зберігати масштабований розмір об’єкта в діапазоні 10-300.
Фіксований масштаб сцени: масштаб сцени для import об’єктів.
Одиниці вимірювання: це лише візуальні позначки одиниць. Фактичне масштабування залежно від одиниць не виконується.
Вертикальна синхронізація :
Гамма-корекція: червоний/зелений/синій.
Використовувати тональне відображення ACES : використовувати тональне mapping ACES.
Увімкнути властивості VoxTree ПКМ : увімкнути або вимкнути вікно властивостей ПКМ у кімнаті скульптур. Вікно також можна вимкнути, призначивши гарячу клавішу у вікні Windows→Спливаючі вікна→Властивості гучності тригера.
Дозволити навігацію за матеріалами за допомогою перетягування ЛКМ/ПКМ у вікні перегляду: Дозволити навігацію за матеріалами за допомогою перетягування ЛКМ/ПКМ у вікні перегляду.
Модулятор ближньої площини: дозволяє встановити, наскільки близько камера Viewport може підійти до об’єкта. Він налаштовує камеру біля літака, щоб мати можливість рухатися ближче до поверхні.
Карта сфери навколишнього середовища: укажіть, яке сферичне зображення буде використано для відтворення будь-яких впливів навколишнього середовища.
Показати мініатюри import на початковій сторінці .
Розмір сітки екрана: установіть розмір сітки в пікселях.
Підрозділ сітки: це значення представляє кількість підрозділів у сітці екрана. Використовуйте нуль для жодного.
Тип фону: стиль фону сцени.
Фонове зображення: зображення, яке буде використовуватися як фон.
Швидкість масштабування камери: визначає швидкість масштабування камери.
Швидкість обертання камери: визначає швидкість обертання камери.
Закріпити швидкість прокручування шаблону: зафіксувати швидкість прокручування шаблону. Змініть шаблон, який використовується для позначення заморожених областей у меню заморозки.
Колесо миші: виберіть параметр, який потрібно змінити за допомогою коліщатка миші.
Щоб мати можливість прокручувати за допомогою середньої кнопки миші, установіть для «Колеса миші» значення «Збільшити».
Переконайтеся, що для 3 нижніх параметрів «Wheel Zoom… Speed» встановлено значення 1. Якщо масштабування не йде в потрібному напрямку, змініть його на -1.
Ctrl+Коліщатко: Виберіть, який параметр змінити за допомогою Ctrl+Коліщатко миші.
Shift+коліщатко: виберіть параметр, який потрібно змінити за допомогою Shift+коліщатка миші.
Alt+коліщатко: виберіть параметр, який потрібно змінити за допомогою клавіші Alt+коліщатко миші.
Швидкість перспективи масштабування колесом: визначає швидкість перспективи масштабування колесом.
Ортографічна швидкість масштабування колеса: визначає ортографічну швидкість масштабування колеса.
Швидкість UV масштабування колесом: визначає швидкість UV масштабування колесом.
Налаштування 3D-друку
Товщина шару для 3D-друку: товщина шару для export 3D-друку.
Розмір збірки: по X,Y,Z.
Чищення зубів
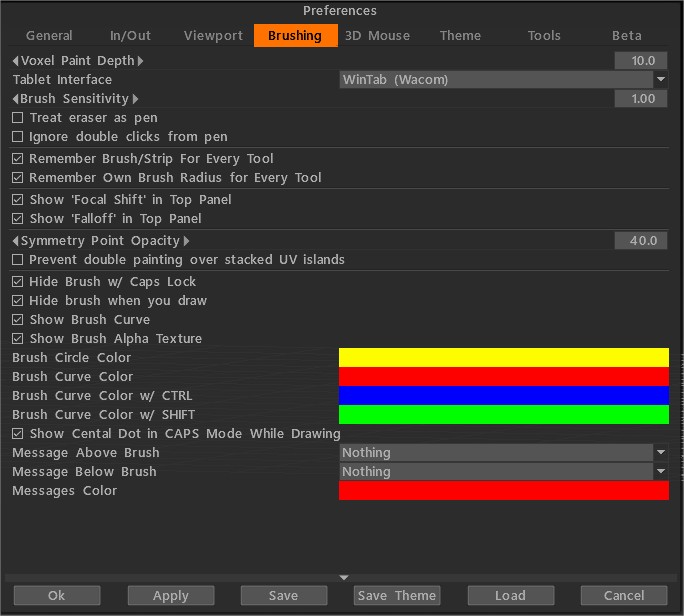
Глибина Voxel малювання: глибина воксельного малювання. Будьте обережні з великою глибиною проникнення кольору, це може викликати артефакти (проникнення на іншу сторону об’єкта, галасливі кольорові плями на шумних поверхнях). Тому ми рекомендуємо малу глибину фарби для шумних поверхонь. Зверніть увагу, більша глибина призводить до повільної роботи.
Інтерфейс планшета: дозволяє вибрати Wintab або планшетний ПК. (Зніміть прапорець «Використовувати Windows Ink» у властивостях планшета Win.)
Чутливість Brush : налаштуйте чутливість пера, якщо ви використовуєте цифрове перо.
Ставтеся до гумки як до ручки .
Ігнорувати подвійні клацання пером: дозволяє починати штрихи подвійним натисканням пера.
Запам’ятовувати Brush/смужку для кожного інструменту: укажіть, чи бажаєте ви, щоб 3DCoat запам’ятовував попередні налаштування кожного разу, коли ви використовуєте Brush.
Запам’ятовувати власний радіус Brush для кожного інструменту: укажіть, чи бажаєте ви, щоб 3DCoat запам’ятовував попередні налаштування кожного разу, коли ви використовуєте цей Brush.
Параметри Brush відображення верхньої панелі: якщо у вас обмежений простір на екрані або ви нечасто користуєтеся « Зміщенням пензля» чи «Зміщенням фокуса», ви можете приховати «Зміщення фокуса» та повзунок «Зниження» на верхній панелі.
- Показати зміщення фокуса на верхній панелі: Показати повзунок «Зсув фокуса» на верхній панелі.
- Показати Falloff на верхній панелі: Показати повзунок «Falloff» на верхній панелі.
Непрозорість точки симетрії .
Запобігати подвійному малюванню над складеними UV острівцями: цей параметр важливий, якщо у вас є складені або дзеркальні UV острівці. Якщо опцію ввімкнено, точка на UV карті може бути зафарбована лише один раз за штрих.
Це корисно, якщо складені острівці не мають межі один з одним (наприклад, тіло – один острівець, руки та ноги – інші дзеркальні острівці). Якщо ви ввімкнете симетрію та цю опцію, руки та ноги не малюватимуться двічі.
Але якщо дзеркальні острови мають спільну межу між собою, увімкнення цього параметра призведе до артефактів біля спільних країв, оскільки той самий піксель присутній по обидва боки краю.
Приховати Brush із блокуванням великих літер: якщо позначено цей параметр, пензель буде постійно приховано в режимі CAPS LOCK; інакше він буде прихований лише під час малювання.
Приховати Brush під час обведення: якщо позначено цей параметр, кисть буде прихована під час малювання.
Показати Brush пензля:
Показати альфа-текстуру Brush :
Колір кола Brush :
Колір Brush :
Колір Brush з CTRL:
Колір Brush пензля з SHIFT:
Показати центральну крапку в режимі CAPS під час малювання:
Повідомлення над Brush:
Повідомлення під Brush:
Колір повідомлень: колір повідомлень під або над пензлем.
Компактний інтерфейс: перемикання між компактним і повним інтерфейсом. Гаряча клавіша TAB.
3D миша
3DCoat підтримує 3D Space Navigator від 3DConnexion. Тут ви можете знайти всі параметри керування 3D-мишею. Якщо ви володієте одним із цих пристроїв, скористайтеся цими налаштуваннями, щоб отримати точний тип контролю, який вам потрібен.
3DCoat отримує всі налаштування з панелі керування пристрою 3D-Connexion, тому немає потреби встановлювати багато налаштувань.
Тож натисніть кнопку налаштувань/меню пристрою та відредагуйте там налаштування. Зверніть увагу, поворот навколо вертикальної осі знаходиться в Розширені налаштування → Режими навігації → Заблокувати горизонт.
Єдині поля, які там не можна редагувати, представлені нижче.
Швидкість масштабування в ортографічному режимі
Модулятор швидкості для трансляції об’єктів : Додатковий модулятор швидкості для трансляції при включеному режимі роботи з об’єктами за допомогою 3D-миші.
Підтримка 3dconnexion : це відео демонструє переваги використання пристрою 3dconnexion, особливо флагманської версії SpaceMouse Enterprise у 3DCoat. Це дозволяє користувачеві переміщатися вздовж шести різних осей одночасно, працюючи плавно. Це подвоює продуктивність, оскільки користувачеві не потрібно зупинятися, переміщатися та продовжувати роботу, постійно працюючи тією ж робочою рукою.
Це також зменшує навантаження на робочу руку від повторюваних дій, розподіляючи навантаження на обидві руки. Це також не дозволяє користувачам відводити руки від клавіатури та не зосереджуватися на моделі.
Використовуйте API 3D-Connexion із 3D-Coat 4.xx: використовуйте старішу версію API 3D-Connexion. Це не рекомендується, оскільки в деяких випадках це може призвести до додаткових затримок, якщо ви використовуєте бездротові пристрої (миша, перо, клавіатура). Але якщо новий API не працює для вас – скористайтеся старішим.
Тема
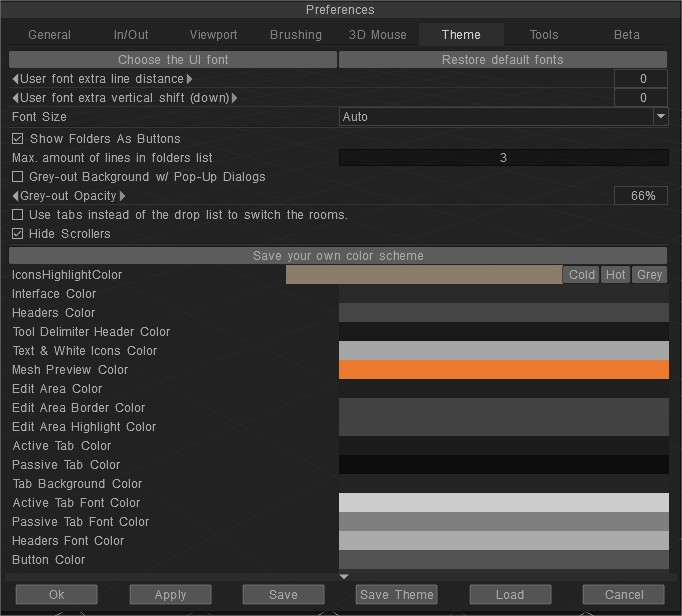
Показати папки як кнопки
Макс. кількість рядків у списку папок: максимальна кількість рядків у списку папок, яка використовується для списків елементів, таких як пензлі, трафарети, стилі тощо.
Розмір шрифту: виберіть розмір шрифту.
Як налаштувати тип шрифту та кольори інтерфейсу від Rygaard
У цьому відео він покаже вам, як налаштувати тип шрифту та кольори інтерфейсу в 3DCoat.
Приховати скролери: приховати панель скролерів.
Використовуйте вкладки замість списку, що випадає: у 3DCoat2023 перемикання кімнати типу коробки з V2021 тепер можна переключити на знайомий тип вкладки в епоху V4 у налаштуваннях середовища.
Збережіть власну колірну схему: натисніть кнопку, потім введіть назву колірної схеми, вона з’явиться в Windows > Колірна тема інтерфейсу користувача, а файл теми буде записаний у «Docs/ 3DCoat/UserPrefs/UI_Color_Themes/TheMeName.json». . Якщо тема з такою назвою існує, її буде перезаписано.
3D-колір кнопки: використовуйте 3D-стиль для кнопок.
Градієнтне меню: використовуйте градієнтну текстуру для меню та фону.
Кольори дисплея: змінюйте кольори, щоб персоналізувати свою тему.
Усі параметри теми і макета інтерфейсу в цих розділах налаштувань дозволяють точно розробити вигляд і макет усього інтерфейсу. Немає двох людей, які люблять однакові речі, тому ці параметри були надані, щоб дозволити вам налаштувати «Вигляд і відчуття» 3DCoat саме так, як вам подобається.
Інтерфейс користувача повністю настроюється. За замовчуванням під час встановлення присутні три теми інтерфейсу користувача.
Це «темний», «сірий» і «світлий».
Ви можете змінити інтерфейс, перейшовши до Редагування–>Параметри–>Завантажити; вас буде спрямовано до папки з назвою «OptionsPresets». У ній є 3 файли .xml, кожен з яких відповідає темі. Щоб завантажити теми, просто виберіть один файл .xml і натисніть «Відкрити».
Ви можете редагувати багато інших частин інтерфейсу користувача, створити власну тему інтерфейсу користувача та зберегти її як файл .xml.
Просто перейдіть до Редагувати → Налаштування.
Тут ви можете налаштувати колір тексту, фону інтерфейсу, заголовка, кнопок, сітки, фону тощо. Ви також можете ввімкнути або вимкнути стиль кнопки 3D і меню градієнта.
Зрештою, це зроблено, збережіть файл .xml, і всі інтерфейси користувача, гарячі клавіші та інша налаштована інформація збережеться в ньому.
Ви можете завантажити його будь-коли або поділитися з друзями. Просто натисніть кнопку Зберегти на панелі налаштувань.
Ви навіть можете змінити піктограми інструментів на власні, перейдіть до папки встановлення 3DCoat, у шляху texturesicons ви знайдете вихідні PSD-файли піктограм, це «baseicons.psd» і «SmallIcons. psd”; відкрийте файл PSD у Photoshop і намалюйте власні значки.
Коли закінчите, збережіть їх у форматі DDS, збережіть назву та замініть оригінальні «baseicons.dds» і «SmallIcons.dds».
Наступного разу, коли ви запустите 3DCoat, він завантажить нові значки.
Межі (доступно лише для версії 4.9.#)
Змініть контрастний колір тла панелей, елементів керування та вікон.
Інструменти
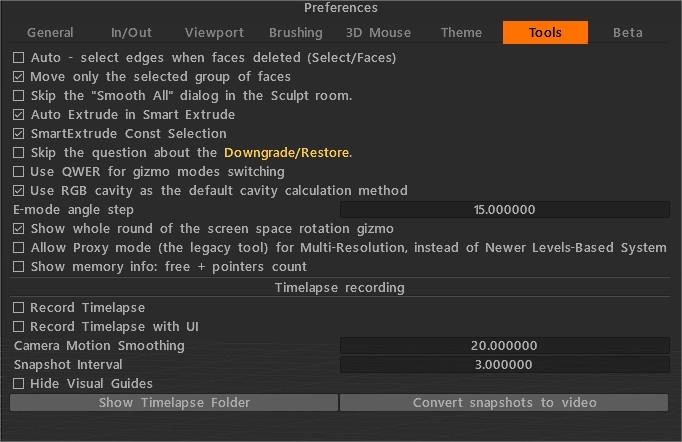
Автоматично вибирати краї, коли грані видаляються (Вибір/Грані): коли ви видаляєте вибрані грані, обмежувальні краї будуть виділені. Вимкніть його, якщо вам не потрібно вибирати краї.
Перемістити лише вибрану групу облич.
Пропустити діалогове вікно «Згладжувати все» в кімнаті скульптур: якщо цей параметр увімкнено, діалогове вікно «Згладжувати все» не відображатиметься. Згладжування буде виконано лише один раз.
Автоматичне видавлювання в Smart Extrude: автоматичне видавлювання після нового виділення.
SmartExtrude Const Selection: вибір увімкнено весь час.
Пропустіть запитання про повернення/відновлення рівня: коли ви клацаєте кеш/відновлення з VoxTree, вас запитають, чи справді він вам потрібен. Якщо цей параметр увімкнено, запитання не з’являтиметься.
Використовуйте QWER для перемикання режимів gizmo: використовуйте його, щоб увімкнути/вимкнути використання QWER для перемикання режимів gizmo.
Перемістити лише вибрану групу облич.
Використовувати порожнину RGB як метод розрахунку порожнини за замовчуванням: нову порожнину RGB було представлено як можливий метод розрахунку за замовчуванням. У цьому випадку багатодіапазонна порожнина буде розрахована на GPU, а в UI умов/розумних матеріалів з’явиться додатковий контроль – «Ширина порожнини». Це дозволяє змінювати ширину порожнини/згладжувати в реальному часі, що дуже важливо для реалістичного текстурування PBR .
Ширина порожнини (з використанням порожнини RGB) може використовуватися для розумних матеріалів для кожного шару окремо. Кожен шар матеріалу має власні налаштування ширини порожнини. Це забезпечує набагато кращий ефект для «старіння» матеріалів, як-от кілька різних «постарілих» шарів фарби.
Порожнина RGB — це багатодіапазонна текстура порожнини, кожен канал відповідає іншій шкалі порожнини. B — локальна порожнина, G — порожнина середнього діапазону, R — порожнина далекого діапазону. Запікає кривизну з радіусом 1, 20 і 100 до каналів RGB відповідно.
Якщо у вас уже є старий шар порожнини в сцені, вам потрібно видалити його, щоб використовувати цю функцію. Це дуже важлива функція для зафарбовування PBR поверх текстури/сітки.
Якщо порожнину RGB увімкнено за замовчуванням і ви завантажуєте сцену з шаром порожнини старого стилю, Coat попередить вас, що краще повторно обчислити порожнину, щоб отримати кращий контроль.
Показати весь круг гізмо обертання простору екрана: активуйте це, якщо гізмо «Вибір/перетворення» не завжди повністю доступне (як ви бачите на малюнку), де стрілки показують, де можна взаємодіяти з гізмо, а коли ні.
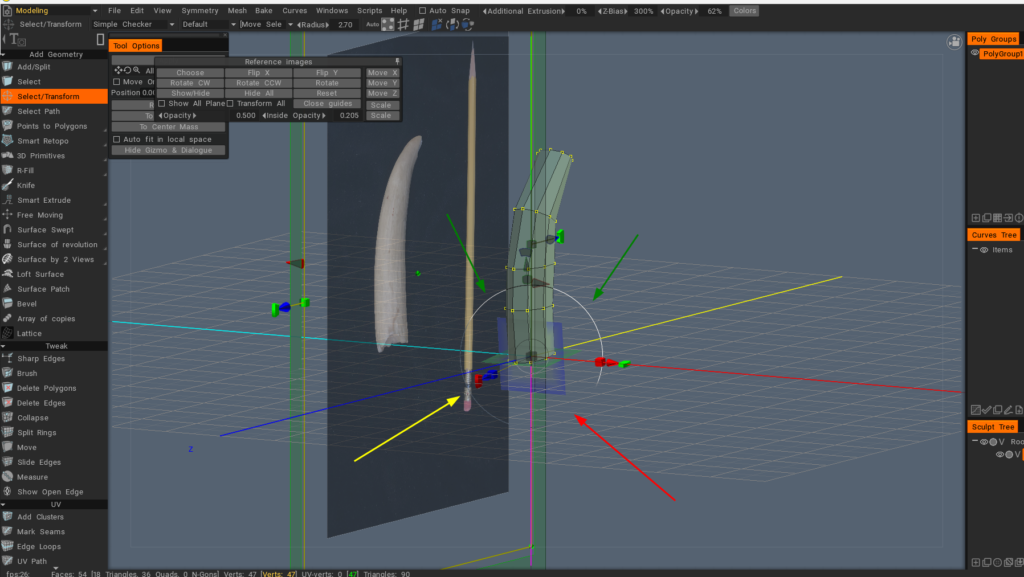
Дозволити режим проксі (застарілий інструмент, натомість використовуйте мультироздільність): це неактивний режим, що запобігає протиріччям між проксі-сервером або процедурними об’єктами з різнороздільністю. Старий метод режиму кешування/проксі вимкнено за замовчуванням.
Показати інформацію про пам’ять: вільна + кількість вказівників: це корисно, якщо ви шукаєте витоки пам’яті та досліджуєте її використання.
Бета
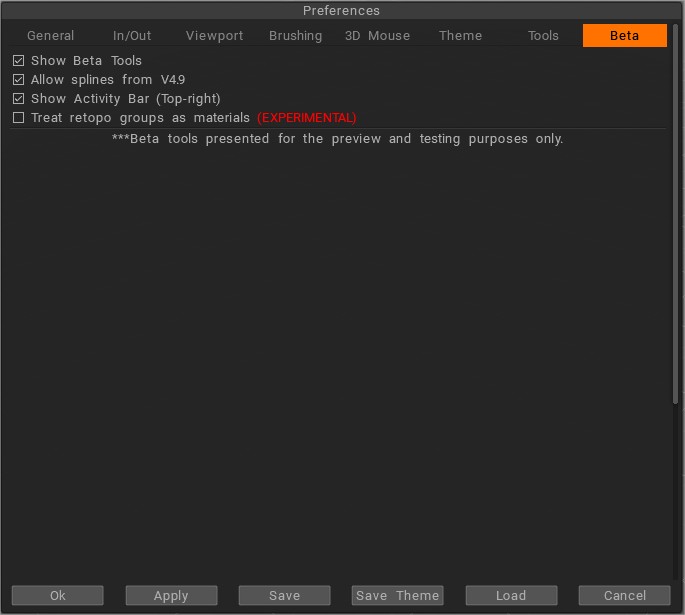
ShowBetaTools: ми рекомендуємо вам завжди вмикати цю опцію, оскільки 3DCoat постійно вдосконалюється шляхом виправлення помилок та інших оновлень. Перегляд і використання бета-версій інструментів і функцій дозволяє вам випробувати будь-які нові виправлення та отримати розширений погляд на функції, які не будуть присутні до наступного великого випуску 3DCoat.
Дозволити об’ємне Painting:
Дозволити сплайни з версії 4.9: увімкнути стару версію сплайнів на електронній панелі. Також буде доступна нова версія сплайнів.
Показати панель активності (вгорі праворуч).
Розглядайте retopo групи як матеріали ЕКСПЕРИМЕНТАЛЬНА Розглядайте retopo групи як матеріали замість об’єктів. Використовуйте цей параметр на свій страх і ризик, це не звичайний робочий процес 3D-Coat. За замовчуванням групи retopo будуть запікатися як об’єкти.
Бета-версії інструментів представлені лише для попереднього перегляду та тестування. Вони є важливою частиною 3DCoat 2022. Вони можуть бути вимкнені у V4.9xx після випуску 3DCoat 2022.
 Українська
Українська  English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Português
Português Italiano
Italiano Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 (台灣)
中文 (台灣) Dansk
Dansk Slovenčina
Slovenčina Türkçe
Türkçe Nederlands
Nederlands Magyar
Magyar ไทย
ไทย हिन्दी
हिन्दी Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Eesti
Eesti Čeština
Čeština Română
Română Norsk Bokmål
Norsk Bokmål